Create a custom Odoo Module
Odoo (previously known as OpenERP) is business management software including ERP, CRM, e-commerce, billing, accounting, manufacturing, warehouse, project management, and inventory management. It has an open source “community” version under the LGPLv3 license and an enterprise version under commercial license.
Prerequisites
PyCharm Configuration
After downloading and installing Odoo and PyCharm we need to create our new virtual environment. With this virtual environment we can see reflected the changes on the code instantly, otherwise we will need to restart the service off Odoo on every change we perform.
We start creating a new project on PyCharm. By default, PyCharm will create a new Virtual environment to the project.
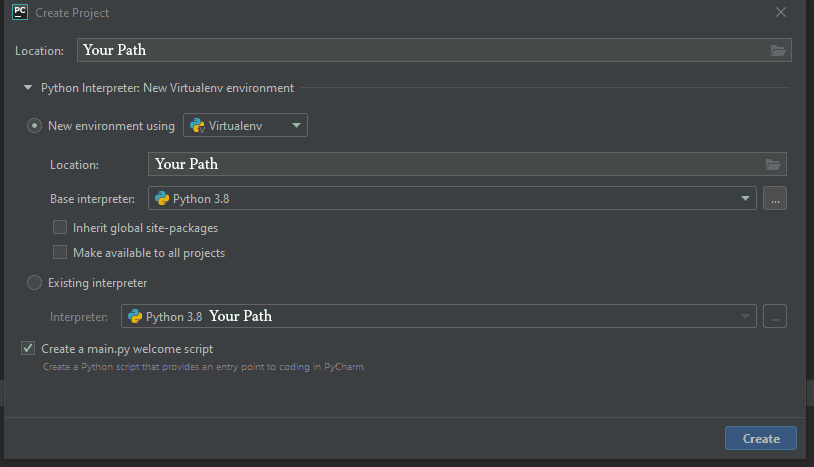
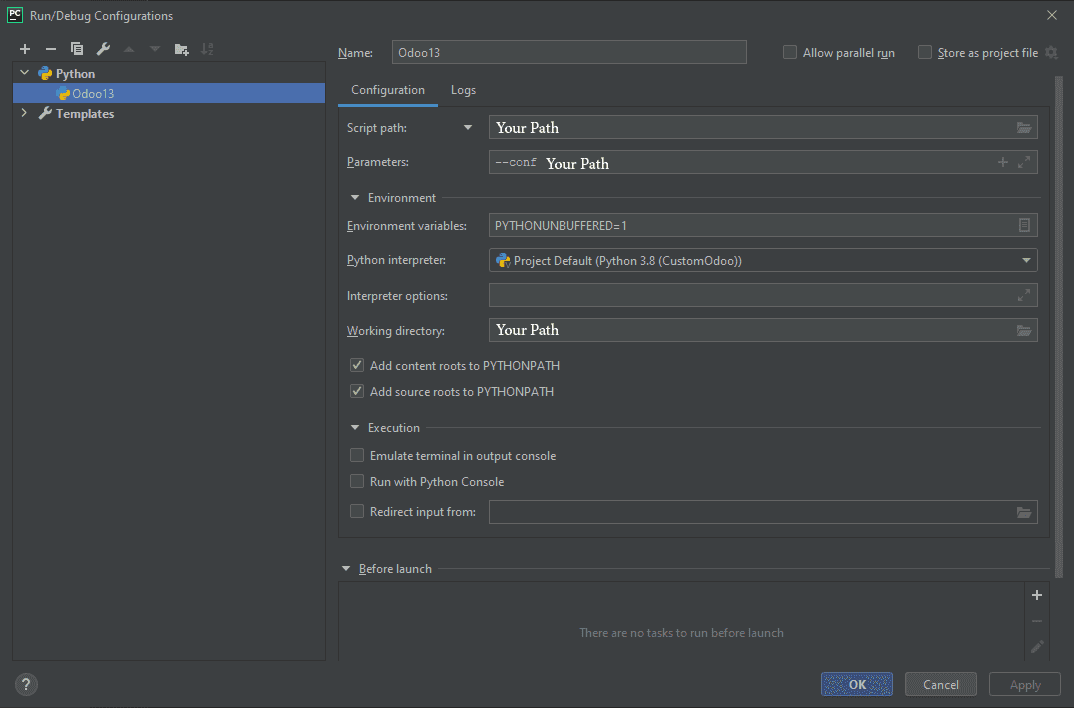
After creating the project, we need to setup the Run/Debug configurations with the following information:
Script Path: [PATH to odoo-bin]
Parameters: --conf [PATH to odoo.conf]
Now we need to install all the modules that Odoo needs to run, these modules are:
| Package | Version |
|---|---|
| Babel | 2.8.0 |
| certifi | 2020.6.20 |
| chardet | 3.0.4 |
| decorator | 4.4.2 |
| docutils | 0.16 |
| html2text | 2020.1.16 |
| idna | 2.10 |
| Jinja2 | 2.11.2 |
| lxml | 4.5.2 |
| MarkupSafe | 1.1.1 |
| passlib | 1.7.2 |
| Pillow | 7.2.0 |
| polib | 1.1.0 |
| psutil | 5.7.2 |
| psycopg2 | 2.8.5 |
| PyPDF2 | 1.26.0 |
| pypiwin32 | 223 |
| python-dateutil | 2.8.1 |
| pytz | 2020.1 |
| pywin32 | 228 |
| reportlab | 3.5.49 |
| requests | 2.24.0 |
| six | 1.15.0 |
| urllib3 | 1.25.10 |
| Werkzeug | 0.11.15 |
You can install these modules via Pip, whl files, requirements.txt or by using the pipfile
Install from requirements.txt
> pip install -r [PATH to requirements.txt]Install from Pipfile
> pipenv installCustom Module
A Odoo module is a set of business logic which helps to enhance the existing functionality or add some new functionality in Odoo.
Odoo.conf
To add our custom module to Odoo first we need to make a few changes to the odoo.conf file.
- Firs we need to specify where our custom module will be stored.
addons_path: [Default PATH], [Custom PATH]- Next, we need to set a new port for the http port
http_port = 8070Module Structure
An Odoo module can contain a number of elements:
Manifest:_ The manifest file serves to declare a python package as an Odoo module and to specify the module metadata. This file is called __manifest__.py and contains a single python dictionary. Learn more about the manifest file here.
Business objects: Declared as Python classes, these resources are automatically persisted by Odoo based on their configuration.
Data files: XML or CSV files declaring metadata (views or workflows), configuration data, demonstration data and more.
Web controllers: Handle requests from web browser.
Static web data: Images, CSS or JavaScript files used b the web interface or website.
Basic Example
Manifest
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-{ 'name': 'Res Partner Services', 'version': '1.0', 'description': 'Custom module for Odoo ERP', 'summary': 'Custom module for Odoo ERP', 'author': 'Jhon Doe', 'category': 'Generic Modules/Inventory Control', 'website': 'http://example.net/', 'license': 'GPL-2', 'depends': ['base'], 'init_xml': [], 'demo_xml': [], 'data': ['respartner.xml'], 'installable': True, 'active': True}respartner.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><odoo> <record id="resPartnerId" model="ir.ui.view"> <field name="name">partner.partner.inherit</field> <field name="model">res.partner</field> <field name="inherit_id" ref="base.view_partner_form" /> <field name="arch" type="xml"> <notebook position="inside"> <page string="Sessions"> <group> <field name="service"/> <field name="url"/> <field name="user"/> <field name="password" password="True"/> </group> </page> </notebook> </field> </record></odoo>respartner.py
from odoo import fields, models, api
class Partner(models.Model): _inherit = 'res.partner'
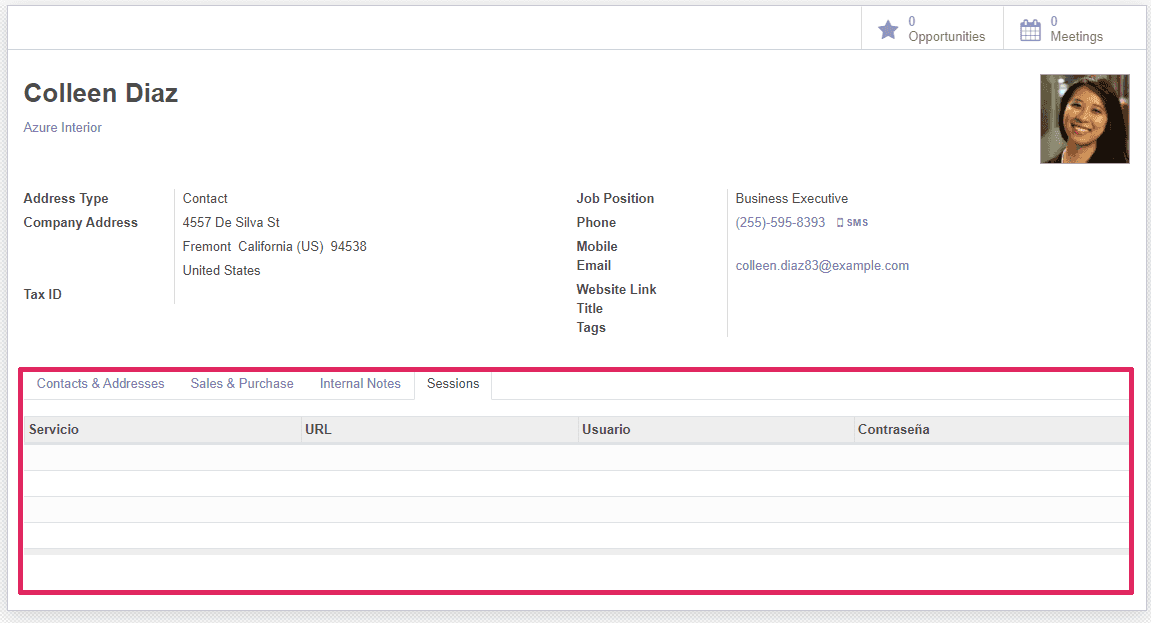
service = fields.Char(required=False, string="Service") url = fields.Char(required=False, string="URL") user = fields.Char(required=True, string="User") password = fields.Char(required=True, string="Password")This code should output 4 custom inputs on the contacts view.
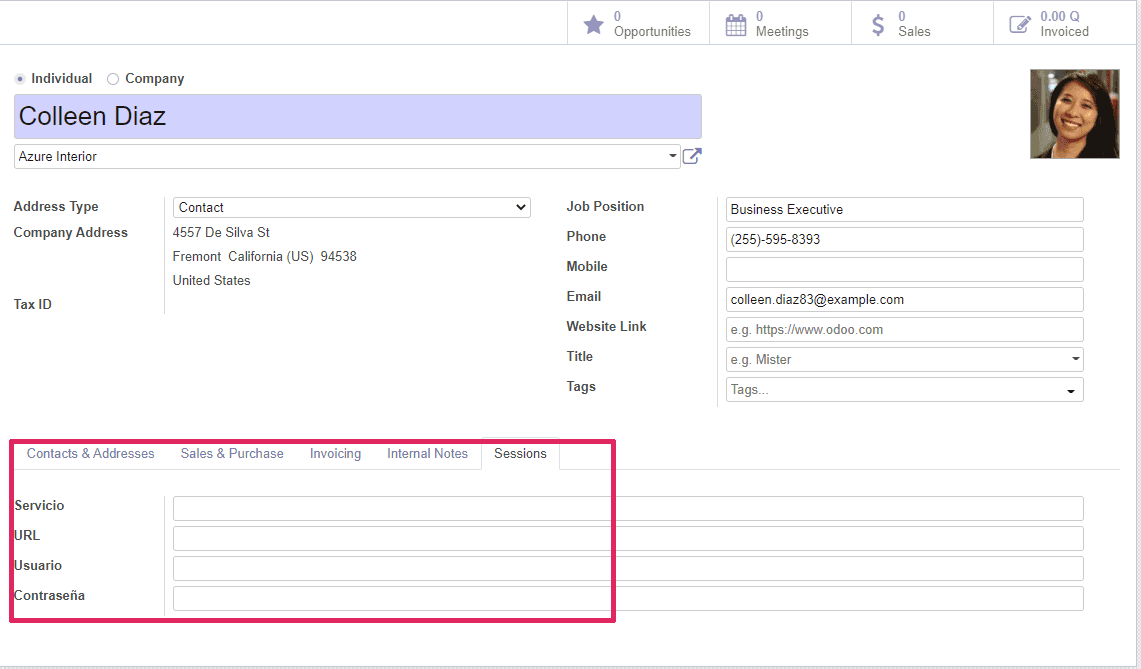
Tree Input Example
respartner.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><odoo> <record id="resPartnerId" model="ir.ui.view"> <field name="name">res.partner.inherit</field> <field name="model">res.partner</field> <field name="inherit_id" ref="base.view_partner_form" /> <field name="arch" type="xml"> <notebook position="inside">
<page string="Sessions"> <field name="partners"> <tree> <field name="partner_id" invisible="1" /> <field name="service"/> <field name="url"/> <field name="user"/> <field name="password" password="True"/> </tree> </field>
</page>
</notebook> </field> </record></odoo>respartner.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-from odoo import fields, models, api
class Partner(models.Model): _inherit = 'res.partner'
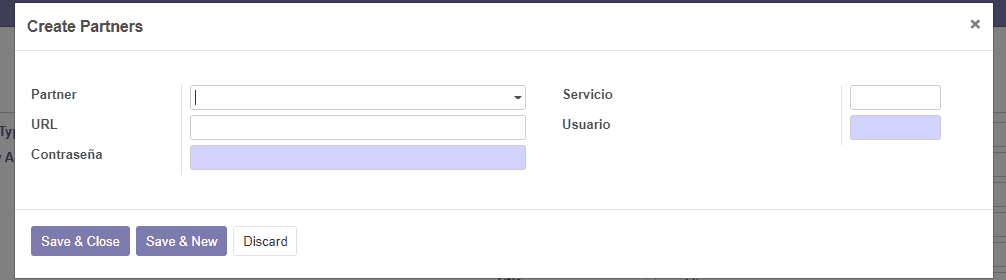
partners = fields.One2many('res.partner.services.list', 'partner_id', string='Partners')
class PartnerList(models.Model): _name = 'res.partner.services.list' _description = 'Service List'
partner_id = fields.Many2one('res.partner.services', strin='Partner') service = fields.Char(required=False, string="Service") url = fields.Char(required=False, string="URL") user = fields.Char(required=True, string="User") password = fields.Char(required=True, string="Password")Now you should be able to add multiple Services to the contacts view.