“Smart business need Business Intelligence”
-Georg Gottlob
Business intelligence or simply BI is a set of strategies, applications, data, products, technologies, and technical architectures which are focused on the administration and creation of knowledge about the environment, through the analysis of existing data in an organization or company.
The main task of Business Intelligence is to provide decision support for business activities based on empirical information.
BI systems differ from operational systems in that they are optimized for obtaining and disseminating data. ETL processes (Extraction, Transaction and Loading) are responsible for nurturing BI systems.

Origin
The term Business Intelligence was coined by H. P. Luhn (IBM) in 1958. Luhn defined intelligence as “the ability to understand the interrelationships of facts presented in such a way that they guide actions towards an objective” and Business as “A collection of activities carried out for many purposes, be it science, technology, commerce, industry, law, government, etc.
Definition
The definition of Business Intelligence has changed a bit throw the years, some of the more significant definitions are listed below:
H. P. Luhn (1958): An automatic system that is developed to disseminate information to the different sections of any organization, scientific industry, or government.
Howard Dresner (1989): Set of concepts and methods to improve business decision making using fact-based systems.
Salomon Negash (2004): They are systems that provide actionable information delivered at the right time, in the right place and in the right way to aid decision-making.
Kevin Roebuck (2011): An integrated, company-specific IT solution used for managerial decision making.
BI Features
Objective: The main objective of BI is to provide decision support for specific objectives.
Bases: BI decisions are mainly based on empirical information, in addition to this empirical background, BI also uses different types of knowledge and theories to generate information.
Realization: support in decision-making must be carried out in a system that uses information and communication technologies (ICT).
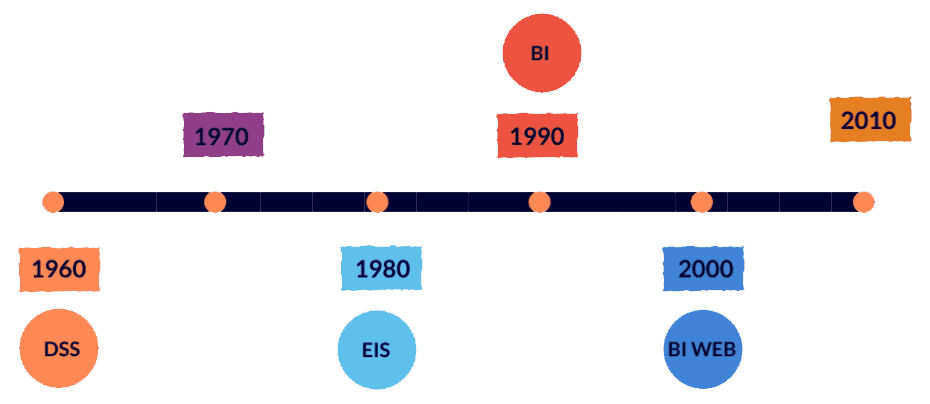
BI Timeline
As already mentioned above, the origin of the term Business Intelligence emerged in 1958, based on the availability of data we can distinguish different eras of BI.
1958-1980: The origins of BI are developed mainly under decision support systems (DSS).
1980-1990: Later in the 80s the executive information systems (EIS) emerged.
1990-2000: The term BI became popular in the 1990s and was understood primarily as data-driven decision support supported by the development of Data Warehouse and the use of online analytical processing (OLAP).
2000-Present: The rise of the internet has made BI tools available to any organization.
BI Challenges
- Improved process integration or understanding, work consignment, and process mining.
- Application of new organizational structures.
- New data sources (Web data, semi-structured data, text).
- New methods for new data types (text mining, opinion mining).
- Use of IT tools: SAAS, Big Data, Cloud.
- New devices: mobile devices, decision support in real time.
Terminology
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT)
Information and communication technologies (ICT) are the result of bringing computing and telecommunications into interaction. All to improve the processing, storage, and transmission of information.
OLTP
OLTP (On-Line Transaction Processing) is a type of processing that facilitates and manages transactional applications.
OLAP
OLAP (On-Line Analytical Processing) is a solution that allows obtaining large amounts of data using multi-dimensional queries.
Data Warehouses
A Data Warehouse is a system that aggregates and combines information from different sources in a single, centralized repository; commonly used for business analytics, data mining, artificial intelligence, or machine learning.
Dimensions
The dimensions (also called entity, perspective, characteristic, master data, etc.) are the groups of data that allows identifying who, when or where a business operation or transaction is generated.
Metrics
Metrics (also called KPIs, indicators, values, etc.) are numerical values generated in one or more transactional business operations.